The DC servo motor is a special purpose DC motor in the automatic control system. It is also called an actuator motor. It can convert the input voltage signal into mechanical signals such as angular displacement and angular velocity on the shaft. The working principle, basic structure and internal electromagnetic relationship of the DC servo motor are the same as those of the general-purpose DC motor.
The control power of the DC servo motor is DC voltage, which is divided into ordinary DC servo motor, disc armature DC servo motor, hollow cup DC servo motor and slotless DC servo motor. Ordinary DC servo motors have two basic structural types: permanent magnet and electromagnetic. Electromagnetic type is divided into four types: excitation, shunt, series excitation and compound excitation. The permanent magnet type can be regarded as the other type.

Features: The rotor has a small diameter and a large axial dimension; the moment of inertia is small, so the response time is fast. However, the rated torque is small and generally must match the gear reduction device. It is used in small CNC machines for high speed and light load.
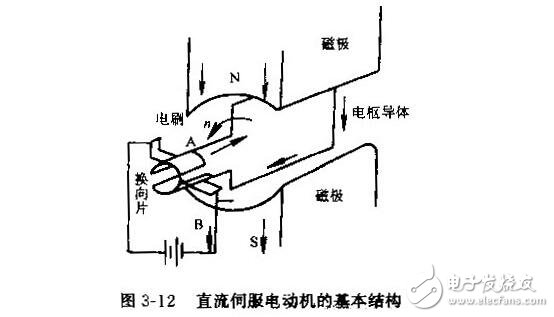
1. Basic structure of DC servo motor
The picture shows the structure of the DC servo motor, which mainly includes three parts: stator, rotor, brush and commutator.
2. Classification of DC servo motors
(1) According to the structure of the motor itself, it can be divided into the following categories:
The improved DC servo motor rotor has smaller moment of inertia, stronger overload capability and better commutation performance.
The small inertia DC motor minimizes the moment of inertia of the rotor and achieves the best fast characteristics.
The permanent magnet DC servo motor can work for a long time under large overload torque, with large moment of inertia and no excitation circuit loss, which can be operated at low speed.
The brushless DC motor consists of a synchronous motor and an inverter, and the inverter is controlled by a rotor position sensor mounted on the rotor.
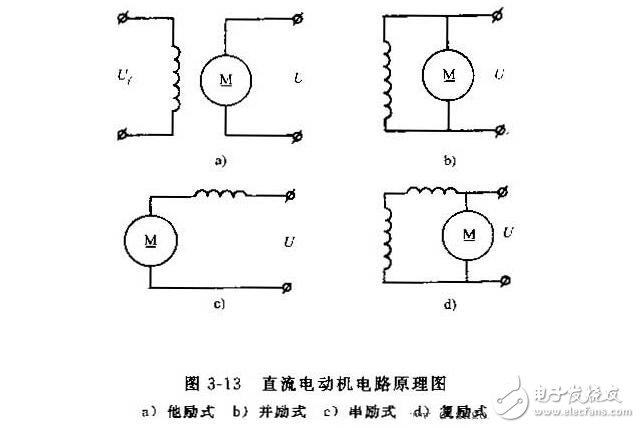
(2) According to the excitation mode of the DC winding of the DC motor, it can be divided into four types: the excitation type, the shunt type, the series excitation type and the compound excitation type.
Characteristics of DC servo motorThe structure of the DC servo motor is the same as that of a general DC motor, but it is made to be elongated in order to reduce the moment of inertia. Its field winding and armature are powered by two separate power supplies. There are also permanent magnets, that is, the magnetic pole is a permanent magnet. Usually, the armature control is used, that is, the excitation voltage f is constant, the established magnetic flux Φ is also a fixed value, and the control voltage Uc is applied to the armature, and the wiring diagram is as shown in the following figure.
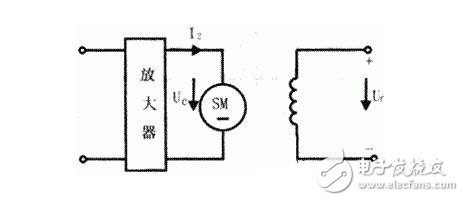
DC servo motors, usually used in systems with slightly higher power, typically have an output power of 1W-600W.
DC servo motors are divided into the following types:
General DC servo motor
Slotless armature DC servo motor
Hollow cup armature DC servo motor
Printed winding DC servo motor
Brushless DC servo motor
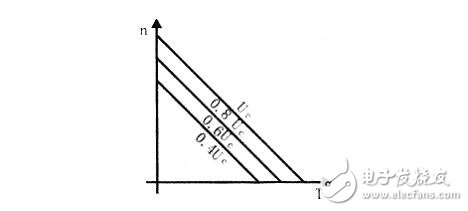
The mechanical characteristics of the DC servo motor (n=f(T)) are the same as the DC-excited motor, which is also expressed by:
n=Uc/KE·Φ-Ra/KE·KT·Φ·T
The figure below shows the mechanical characteristics of a DC servo motor at different control voltages (Uc is the rated control voltage).
It can be seen from the figure that under a certain load torque, when the magnetic flux is constant, if the armature voltage is raised, the motor speed will increase; conversely, lowering the armature voltage, the speed will decrease; when Uc=0, the motor will be Stop immediately. To reverse the motor, change the polarity of the armature voltage.
Technical parameters of DC servo motor1. Rated power refers to the rated value of the output power on the motor shaft, that is, the output power when the motor is running under rated conditions. Allows the motor to run continuously for a long period of time at rated power without overheating.
2. Rated voltage refers to the voltage rating that should be applied to the field winding and armature control winding when the motor is running under rated conditions.
3. The rated current refers to the current in the winding when the motor is driven at the rated power. The rated current is generally the maximum current allowed by the motor for long-term continuous operation.
4. The rated speed is also called the maximum speed, which refers to the speed at which the motor is rated at the rated voltage. The range of the speed of the DC servo motor is generally below the rated speed.
5. Rated torque refers to the output torque when the motor is running under rated conditions.
6. Maximum torque refers to the maximum torque that the motor can output in a short time, which reflects the instantaneous overload capability of the motor. The instantaneous overload capability of the DC servo motor is relatively strong, and its maximum torque is generally 5-10 times of the rated torque.
7. Electromechanical time constant Ï„j and electromagnetic time constant Ï„d
It reflects the length of the two transition process times of the DC servo motor. Τj is typically less than 20ms, τd is typically less than 5ms, and the ratio between the two is typically greater than three, so DC servo motors can generally be viewed as first-order inertia.
8. The thermal time constant is the time required for the motor winding to rise to 63.2% of the rated temperature rise.
9. The damping coefficient is also called the internal damping coefficient, and the reciprocal is the slope of the mechanical characteristic curve.
Characteristic parameters of DC servo motor(1) The torque-speed characteristic curve is also called the working curve.
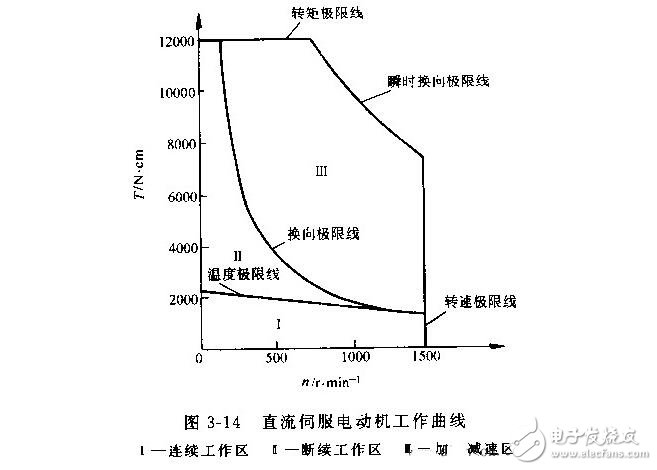
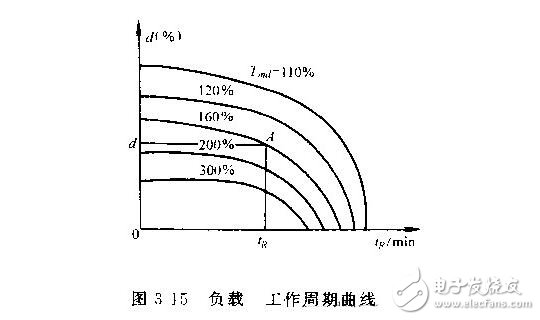
(2) Load-work cycle curve
HQD Vape pen, Wholesale HQD Vape, HQD Manufacture
Shenzhen Xcool Vapor Technology Co.,Ltd , http://www.xcoolvapor.com