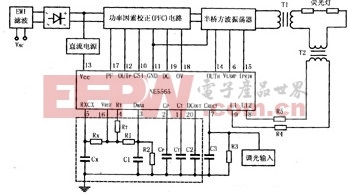
The NE5565 controller includes two switching power supply control circuits: the first is a PFC boost converter controller, which can increase the electronic ballast power factor to above 0.99, the current harmonic distortion is extremely low, and the AC transient voltage Protection is provided; the second is a half-bridge oscillator circuit that converts the DC high voltage of the PFC output into a high frequency AC voltage. The half-bridge controller drives two external high-voltage power MOSFETs for lamp current regulation, peak lamp voltage limiting, and power switch protection. The NE5565 has an operating temperature range of 0-85 °C.
The main features of the NE5565 are:
â— The same chip can complete PFC and ballast dimming control;
â— AC current harmonic distortion is very low;
â— Variable frequency mode;
â— Programmable preheating and ignition to achieve three-step soft start;
â— Lamp overvoltage protection;
â— It can eliminate the overshoot generated when the load is cut off and realize overvoltage protection.
The typical application circuit of the NE5565 is shown above. T1 is a high-frequency transformer of a half-bridge oscillator, and T2 is a lamp current detecting transformer.
A port is an interface through which data is transferred between a computer and other devices (such as printers, mice, keyboards or monitors), networks, or other directly connected computers.
For the CPU, the port is used as one or more memory addresses for sending or receiving data. Dedicated hardware, such as an additional circuit board, places the data from the device in a memory address, and sends the data from the memory address to the device. Ports can be dedicated for input and output only. The port usually receives a specific type of plug for a specific purpose. For example, serial data interfaces, keyboards, and high-speed network ports all use different connectors, so it is impossible to plug the cable into the wrong port.
In programming, a port is a "logical connection location", especially in the Internet Protocol TCP/IP, a way for the client program to be assigned to a special service program on the computer. High-level applications that use TCP/IP protocols such as web protocol and hypertext transfer protocol have specially designated ports. From the perspective of port allocation, ports are divided into two categories: fixed ports and dynamic ports: Fixed ports (0~1023): use a centralized management mechanism, that is, subject to the assignment of ports by a management organization, which is responsible for issuing these assignments . Because these ports are closely tied to some services, we will often scan these ports to determine whether the other party has enabled these services, such as TCP 21 (ftp), 80 (http), 139 (netbios), UDP 7 (echo), 69 (tftp) and other well-known ports; Dynamic ports (1024~49151): These ports are not fixedly bound to a certain service. The operating system dynamically allocates these ports to each process, and the same process is allocated twice It is possible to assign to different ports. However, some applications are reluctant to use the dynamic ports allocated by the operating system. They have their own "branded" ports, such as port 4000 of the oicq client and port 7626 of the Trojan Binghe, which are all fixed and famous.
Pon Port,Nms,Web,Fttx Fttb Application,Fiber Optic Equipment
Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com