Every time you want to help your mobile phone, computer, or other various electrical appliances, you must always pick up a charging cable. There are more charging cables, and you often get the wrong ones. It is very troublesome. Fortunately, more and more electronic products are now using wireless charging technology! As long as you elegantly put your phone on a small, cup-like thing, you can easily recharge it without wiring. What is the principle behind such a powerful technology? Let us explore the mystery together.

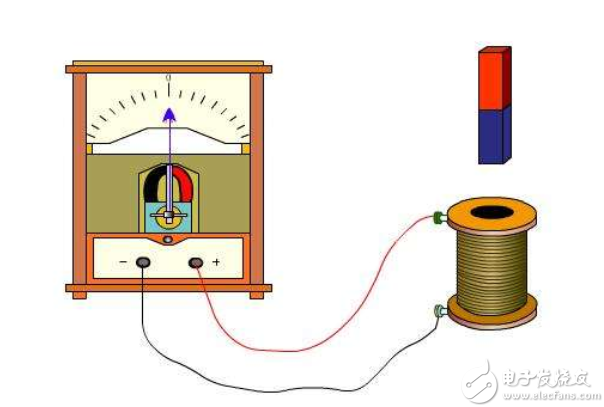
The interaction between electricity and magnetism is generally seen in wireless charging, using the principles of current magnetic effects and electromagnetic induction. In 1819, the Danish scientist Erst observed that if there was a current on a wire, a magnetic field would be generated around it, which would deflect the north arrow. Later generations have further discovered that the wire is enclosed in a ring shape, even wound into a coil, and the generated magnetic field will be stronger and more concentrated. This is called the current magnetic effect.
As for electromagnetic induction, it was discovered by Faraday in 1831. Let a magnet or other source of magnetic field approach a coil without current, and an induced current will be generated on the coil, called electromagnetic induction. It is worth noting that the key point of electromagnetic induction is that the magnetic field needs to change, for example, the magnet is getting closer and closer (it is more and more far away). If the applied magnetic field remains constant, there will be no induced current.
In summary, the current magnetic effect is that the flow of current generates a magnetic field around, and the electromagnetic induction is a constantly changing external magnetic field that causes the coil to generate an induced current.
Use electromagnetic induction to charge
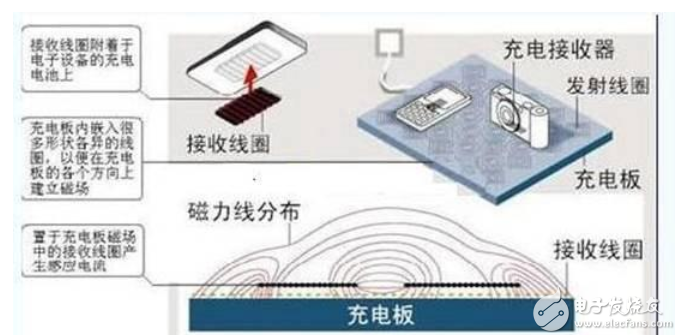
These two physical phenomena can be used simultaneously to perform wireless charging. Current wireless charging devices include a charging stand, which is actually a coil. When the charging stand is connected to the household plug, a magnetic field is generated around the coil due to the current magnetic effect. The electronic product to be charged also has a coil inside. When it is close to the charging stand, the magnetic field of the charging stand will pass electromagnetic induction to generate an induced current on the coil of the electronic product. The induction current is directed to the battery, which completes the wireless charging between the charging stand and the electronic product.
You may ask, is the magnetic field not changed to have electromagnetic induction? However, the distance between the charging stand and the charged object remains the same, so why is there electromagnetic induction? It turns out that the electricity flowing out of the household outlet is AC, which means that the direction of the current changes alternately, and then the flow follows, and the flow is reversed for a while. Because of this, the magnetic field generated by the charging socket coil is constantly changing direction, and it does not remain unchanged, which is in line with the requirements of electromagnetic induction.
Recently, more and more smart phones and tablets have begun to provide wireless charging functions, but unfortunately, when charging them, the charging efficiency will drop significantly as long as they are farther away from the charging stand. Even with the latest technology, the charging distance can't exceed 5 cm. In fact, most mobile devices that can be wirelessly charged are all placed on the charging stand, and the wireless with the imaginary There is still some difference in charging.
Using resonance to lengthen the charging distance In order to increase the distance and charging efficiency of wireless charging, scientists are trying to use the principle of magnetic resonance for wireless charging. Add some special components such as capacitors and inductors to the circuit. After proper connection, a resonant circuit will be formed. This is like the tuning tool that the instrument line must have—the tuning fork. Tap the tuning fork once, it can continue to vibrate for a while, and similarly, the resonant circuit is briefly energized, and the signal will be generated for a period of time in the circuit.
The tuning fork has the interesting physical properties of resonance. Each tuning fork has its own vocal frequency. When a tuning fork vibrates, if there is another tuning fork with the same vocal frequency nearby, even if it is not directly hit, it will vibrate. The resonance of the tuning fork can be said to achieve the transfer of energy. The resonant circuit can also resonate. Two resonant circuits with the same vibration frequency are put together. When one of them starts to oscillate due to energization, the other circuit will also oscillate and automatically generate a current, and the electric energy is transmitted through the space. This phenomenon is called magnetic resonance and is used for wireless charging. It can make the charging distance reach several meters and the efficiency is also improved. The only difficulty is that it is not easy to adjust the two circuits to exactly the same frequency for a period of time.
In addition to magnetic resonance, some scientists try to charge by the light energy of laser light, or even transmit it through the frequency band of the Wifi network close to the home. I hope that the breakthrough of these technologies will make us more convenient in charging in the future!
The practice of wireless charging in the fields of consumer electronics and electric vehicles, represented by Apple, Samsung, and ZTE, will accelerate the opening of the 100 billion market. A few days ago, some media reported that although the prediction that iphone7 has wireless charging function has not been realized, the new Apple in 2017 will have a high probability of having wireless charging function. At the same time, according to the current situation of wireless charging of enterprise layout, 2017 Wireless charging has not only made breakthroughs in the field of consumer electronics. In the field of domestic electric vehicles, wireless charging will also usher in a big development opportunity. The wireless charging prospect is unlimited, so take a look at the new wireless charging technology!
1. Ultrasonic wireless charging: The effective range is close to 5 meters. A company called uBeam invented a new wireless charging mode that can use ultrasonic waves to transport power to a distance of 15 feet (about 4.6 meters). With such a product, you can use your mobile phone to move around the house while charging while using a dedicated wireless charging kit. Although uBeam's prototype is still cumbersome, the company is working hard to reduce the size and bring it to market as soon as possible. It is reported that many companies have hoped to reach a strategic cooperation with uBeam to provide customers with such wireless space charging services to attract more passengers, including Starbucks, Virgin Atlantic, Starwood Hotels and a number of fast food chains. In addition, uBeam has also communicated with hardware vendors such as Apple and Samsung.
Venture capitalists also seem to see opportunities: People familiar with the matter said the company hopes to seek a total of $50 million in Series B financing, with a valuation likely to reach or exceed $500 million. But uBeam declined to comment. The company received a $10 million Series A round of funding from Upfront Ventures in October last year, and previously received $3.2 million in seed investments from companies such as Andreessen Horowitz and Founders Fund. Many companies have tried real wireless charging before, but most of them failed, and only the magnetic resonance charging was realized. This mode must bring the device close to the transmitter or even directly to the transmitter, so there is no major breakthrough compared to plug-in charging.
uBeam early prototype
However, the endorsements of many big-name investors indicate that uBeam's wireless charging model may have great potential. Specifically, uBeam uses ultrasound-conducting technology, where the transmitter takes power through the electrical system of the socket or building, then converts it into ultrasound, and then transmits the vibration to the device with the built-in receiver—for example, with a wireless charging sleeve. After the mobile phone and receiver are responsible for converting the ultrasonic vibration into electricity, charging the mobile device.
uBeam says that this mode has a charging speed similar to that of a conventional power supply.
This ultrasonic space charging method has several advantages. First of all, this technique is very safe, and it uses ultrasound similar to the ultrasound used to monitor the fetus. In addition, the price of the receiver is also very cheap, about $50, or even lower, and small size. Not only that, but these ultrasounds can also be used to transmit data, so uBeam can also play a role in the Internet of Things.
But what appeals to the average user is that the technology has an effective range of about 15 feet and is equally effective for moving devices. Although smartphones have made significant progress in terms of size and performance, battery life has not improved much, which not only undermines the user experience, but also hinders the development of the entire mobile economy. Therefore, uBeam's technology may contribute to the entire industry. Technology giants such as Apple and Samsung are working hard to solve the charging problem, but they have not made progress. Therefore, they are likely to purchase uBeam. Since uBeam holds a number of important wireless charging patents, these giants may acquire the company at a premium to avoid important technology falling into the hands of competitors.
In the long run, if uBeam's wireless charging protocol really realizes its potential, it means that the wires will gradually disappear. Not only mobile phones, but also other types of electrical equipment will use this technology. To be clear, uBeam is still overcoming some serious technical challenges, and the final product may not be able to meet expectations in terms of price, power, speed and safety. However, if it can really achieve market expectations, it will become a revolutionary technology, which is the result of investors' dreams.
2, wireless charging new technology: Microsoft intends to use focused light to charge If your smartphone appears to be exhausted during the day, people generally feel troubled, most people's solution is to try to remember at night to Their devices are charged. Even if it is done, sometimes it is not enough for people to use it everyday. It is sometimes necessary to charge all day. For this reason, Microsoft Research has developed a potential solution: AutoCharge.
Microsoft researchers describe AutoCharge as a technology that automatically locates and charges computers on their desks. The prototype charger they built can be mounted on the ceiling and has two working modules: a monitoring module that uses Microsoft's Kinect camera to scan objects like smartphones; the other is charging mode, using UltraFire CREE XM-L T6 to focus LED light.
The AutoCharge system uses image-based processing to monitor and track smartphones on the table and automatically charge smartphones. The charger will continue to rotate until it detects an object that looks like a smartphone, and then uses the beam generated by solar power technology to remotely charge the smartphone. In other words, no wires are needed.
AutoCharge establishes a connection via Bluetooth or a LED on the phone and a smartphone. This ensures that charging can be stopped when the battery is fully charged, and that objects that are similar in size and shape to the smartphone cannot be charged. The system automatically shuts down within 50 milliseconds when it recognizes that an object is present between it and the smartphone, causing interference to the charge.
The demand for smart phones for broadband wireless communication, image processing and other aspects has led to an exponential increase in actual power consumption. In the future, the bandwidth of 5G communication will be 10 times higher than that of 4G. The high-definition video technology such as 4K/8K will be gradually applied, and the processing power of CPU and GPU will continue to increase. All of this will lead to an exponential increase in the overall energy consumption of smartphones.
The battery capacity has grown linearly and the demand for energy consumption has gradually widened. Battery technology has been slow to break through and become the biggest bottleneck for terminal use. Battery capacity is growing slowly, with a linear increase of about 15% per year, while energy consumption is exponentially increasing. The gap between energy demand and battery performance is becoming more apparent. The battery performance curve will be seriously derailed from the energy demand curve. Increasing the charging speed has become a key solution for battery life. Fast charging has become a hot spot in the market.
First, the principle of fast charging Fast charging technology will become the standard for mobile phones. Under the premise that the battery capacity cannot be quickly achieved and the mobile phone power consumption is rapidly increasing, the popularization of fast charging technology is particularly necessary. China Information and Communication Research Institute defines fast charging as follows: the average current of charging into the battery in 30 minutes is greater than 3A or the charging capacity is more than 60% in 30 minutes.
The fast charging system includes fast charging standard, fast charging source adapter, interface E-marker chip, charging cable, mobile phone fast charging chip, battery and other parts. Each part must be specially designed for different standards to achieve fast charging function and ensure charging safety.
1, the four charging links of the mobile phone
1) Charging adapter The charging adapter's task is to convert 220V mains to 5V that the mobile phone can withstand (currently, various charging protocols, such as QC and USB PD (Type C interface), are also required to send 9V/ 12V/14.5V or even 20V voltage. We have discussed the topic of charging protocol in the previous public number), and have certain power output capabilities, such as 5V/2A, 9V/1A and so on. The charging adapter belongs to the technical category of AC-DC. The commonly mentioned fast charging chip is a general term for the adapter AC-DC chip and the switch-type charging management chip of the mobile phone (using DC-DC technology as the means), but this article is fast. The charging chip refers specifically to the switch-type charging management chip of the mobile phone.
2) Charging cable The task of the charging cable is to transfer the voltage/current from the adapter end to the mobile phone. Since most of the charging lines are actually USB cables. There is a parameter here that needs to be brought to your attention. According to the USB2.0 standard, the cable needs to have a current capacity of up to 1.8A, so if it is a 5V adapter, the maximum power that the USB2.0 cable can transmit is only 9W.
3) Fast charging chip Its task is to convert the adapter's 5V/9V/12V voltage into the battery voltage, and accurately charge the battery according to the required charging current. From a technical point of view, fast charging chips are the most challenging part of these four links, so the current industry has the ability to provide high-quality and high-reliability fast-charge chips manufacturers are very limited, mainly to Texas Instruments, Fairchild Semiconductor, etc. A few foreign major manufacturers, the domestic Xiqi Microelectronics, Hanergy after years of unremitting independent research and development, has launched a series of fast charge chips, breaking the monopoly of foreign big manufacturers, and has been in each Large mobile phone solution providers and brands are widely used. The specific introduction of the fast charge chip will be explained in detail below.
4) Battery The battery is a very important part of this link. The entire charging process is to make the battery fully and safely charged. The main parameters of the battery include: capacity (mAH, 2000mAH, 3000mAH and 4100mAH common in mobile phones), charge cut-off voltage (currently 4.2V, 4.35V and 4.4V specifications, higher charge cut-off voltage, in the same In the case of battery volume, it usually has a higher battery capacity, so the so-called high voltage battery of 4.35V and above is gradually more widely used on mobile phones, and the maximum acceptable charging current and the like. Among them, the maximum acceptable charging current is generally expressed in nC. For example, a 3000mAH battery, 1C charging speed means that the battery can be fully charged within one hour. The maximum charging current that can be accepted is 3A. If the charging speed of 2C is allowed, then the battery can be fully charged in theory for half an hour. The maximum acceptable charging current at this time is 6A; and so on.
Second, the classic three-stage charging in fact, the process of charging the lithium-ion battery is very similar to the process of discharging water into the washbasin in our life:
The first stage: When you start to discharge water to an empty washbasin, the amount of water will be kept small in order not to let the water splash out; the second stage: wait until the bottom of the washbasin is full of a certain water level before the faucet is opened. It’s bigger, the water in the basin can cushion the rapid influx, so there won’t be splashes; the third stage: when the water level is near the top of the washbasin, we will Gradually reduce the amount of water in order to prevent water from rushing out of the washbasin until it fills the entire basin.
The battery is like this washbasin, except that it stores not water but electric charge. The charging of the battery also has three similar phases:
The first stage: trickle charging. The characteristic of the battery is that when the battery voltage (roughly equivalent to the water level) is very low, the internal lithium ion activity is poor, and the internal resistance is large, so only a small charging current can be accepted (generally around 30 to 50 mA). Otherwise, the battery is prone to heat and aging, which not only damages the battery life, but also has potential safety problems. Therefore, this stage is called trickle charging, and some people call it linear charging or pre-charging.
The second stage: constant current charging. When the battery voltage is higher than 2V, the lithium ion mobility of the battery is fully activated, and the internal resistance is also small, so that it can accept charging with a large current. At this stage, the fast charge chip will provide an acceptable charging current to the battery according to the setting, so the battery will also receive the largest amount of power at this stage, which can account for 70% to 80% of the capacity.
The third stage: constant voltage charging. The battery is a very delicate energy storage component, its battery voltage is not allowed to exceed ±50mV of the cut-off voltage, otherwise there will be safety hazards. Therefore, when the battery voltage is charged close to the charge cut-off voltage, the fast charge chip must be able to automatically reduce the charge current, and control the "water splash" not to exceed the range until the battery is fully charged.
A qualified fast-charge chip must be able to automatically control the charging process to seamlessly switch between the above three stages, depending on the battery voltage, without the aid of other hardware or software.
Ccd Barcode Scanner,Manhattan Barcode Scanner,Ccd Barcode Reader,Handheld Ccd Scanner
Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com