A speaker refers to a device that can convert audio signals into sound. Generally speaking, it refers to the power amplifier provided in the main body of the speaker box or the subwoofer box. After the audio signal is amplified, the sound is played back by the speaker itself to make the sound louder.
The sound box is the terminal of the entire sound system. Its function is to convert the audio electrical energy into corresponding sound energy and radiate it to the space. It is an extremely important part of the sound system, and is responsible for converting electrical signals into acoustic signals for human ears to listen directly.
How the speaker worksTo understand the principle of sound produced by the speaker, we first need to understand the propagation of sound. The propagation of sound requires a medium (vacuum cannot transmit sound); the sound must rely on all gases, liquids, and solids to spread out as a medium. These substances as a medium of transmission are called media. Just like a water wave, you throw a stone on the calm water, and there is a wave on the water surface, and then propagate to the other side for 4 weeks; the sound wave is also formed in this way. The frequency of the sound wave is in the range of 20-20,000 Hz, and can be heard by the human ear; below or above this range, the human ear cannot hear. Waves and sound waves propagate in the same way. Only through the propagation of the medium can the human ear hear the sound. Sound waves can propagate in gases, solids, and liquids.
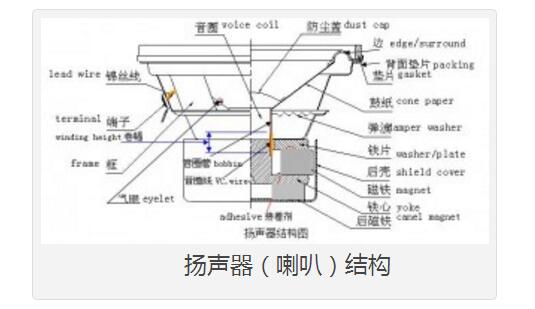
Let me talk about the working principle of the speaker. A horn is a device that converts electrical signals into acoustic signals. It consists of coils, magnets, paper cones, etc. The current (alternating current) of different sizes output by the amplifier moves the coil under the action of the magnetic field through the coil. The coil is connected to the paper cone to drive the paper cone to vibrate, and then the vibration of the paper cone pushes the air to make a sound.
The sound principle of the horn
When the speaker receives the electrical signal output by the sound source device, the current will pass through the coil on the speaker and generate a magnetic field reaction. The current through the coil is an alternating current, and its positive and negative poles are constantly changing; the positive and negative poles will attract each other, and the coil will be attracted by the magnet on the horn to move backward (in the box); the positive pole and the positive pole will repel each other. , The coil moves outward (outside the box). This expanded rhythm will produce sound waves and air currents, and emit sound, which has the same effect as the throat vibration of our speech.
Frequency response curve SPL vs Freq
The frequency range that can be heard by the human ear is 20Hz-20KHz, ("20hz is called infrasound," 20KHz is called ultrasound). The vertical axis of the icon ─ represents the sound pressure level, and the unit is dB. The abscissa of the icon means frequency, the unit is Hz.
The left side of the icon is the frequency response curve of the bass unit, and the right side is the tweeter unit, including the left and right speakers. Several important parameters can be known from the frequency response curve:
Characteristic sensitivity (SPL): The sound pressure measured at a distance of one meter with one watt of electric power, and the average value obtained from four points from the frequency response curve is the average sound pressure.
Effective frequency range (F0 ~ 20KHz): SPL-10 dB, so that a straight line and a curve intersect two points, and the effective frequency range is between these two points. As shown above, the effective frequency range of the speaker is 45Hz ─ 20KHz, the effective frequency range of the bass unit is 40Hz ─ 3KHz, and the effective frequency range of the tweeter unit is 1800Hz ─ 20KHz. The flatter the frequency response curve, the better, and the wider the bandwidth, the better.
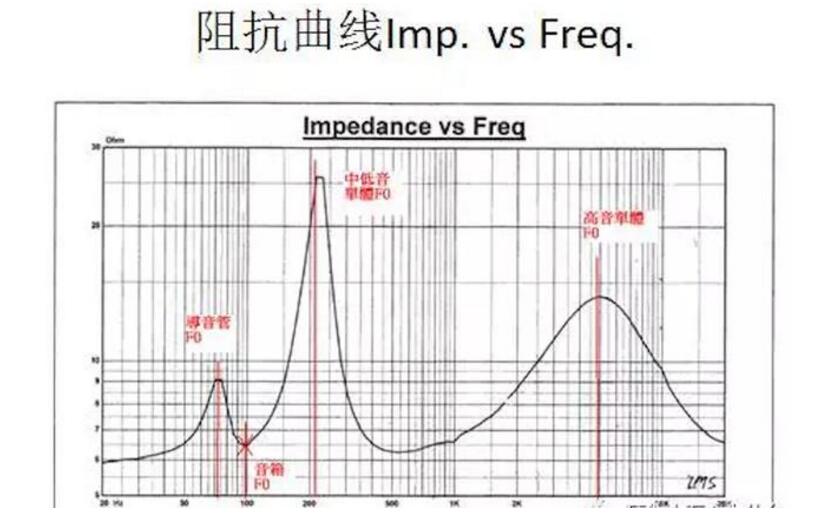
Several important parameters can be known from the impedance curve:
Impedance value (Ohm):
The lowest coordinate corresponding to the lowest point after the peak of the graph is the impedance value.
Minimum resonance frequency (F0):
Single speaker (single peak) ─The point where the peak of the impedance curve corresponds to the abscissa is F0. Speaker horn (double peak)-The point on the abscissa corresponding to the valley between the first peak and the second peak of the impedance curve is Fb, the first peak is the sound tube F0, and the second peak is the single F0. Speaker speaker + tweeter (three peaks)-the point where the peak of the impedance curve and the valley between the peaks corresponds to the abscissa is Fb, and the third peak is F0 of the tweeter.
1. DC impedance (Ohm):
The impedance is measured with a static speaker, so the result is the DC impedance, which is the impedance value of the total length of the copper wire wound on the voice coil. DC impedance is not affected by frequency.
2. AC impedance (Ohm):
The dynamic impedance, that is, the AC impedance value obtained after power-on.
(The tolerance requirement for the voice coil is usually ± 15%.)
3. Standard input power (W): is the rated withstand power of the speaker, which is a guaranteed value.
4. Maximum input power (W): refers to the maximum withstand power of the speaker, only withstand the peak voltage within 1 second, non-guaranteed value.
5. Output sound pressure, also known as sensitivity (dB):
Sensitivity, also called characteristic sensitivity, is generally defined as the sound pressure generated on the reference axis at one meter from the reference point when the speaker is placed on the input of the anechoic chamber baffle plus a signal voltage equivalent to one watt of electrical power at rated impedance , The characteristic sensitivity is expressed in decibel "(dB)" units. The sensitivity of the speaker has a greater relationship with the performance of the speaker vibration system and the magnitude of the magnetic induction in the air gap.
6. Polarity:
Add a pulsed DC signal to the input terminal of the speaker. If the vibration is pushed forward, the positive terminal of the speaker is connected to the positive terminal of the DC voltage, and the negative terminal is the reverse.
The speaker (speaker system) is generally mainly composed of speakers, cabinets and crossovers.
The role of the speaker (commonly known as the speaker) is to convert the electrical signal output by the power amplifier into a sound signal and then radiate it out.
(1) Classification of speakers
There are many ways to classify speakers: they can be divided into electric type, electromagnetic type, piezoelectric type, digital type, etc. according to their transduction method; according to the structure of the diaphragm, they can be divided into single paper cone, composite paper cone, composite horn, and A variety of shafts and so on; according to the shape of the diaphragm can be divided into cone type, dome type, flat type, belt type, etc .; according to the playback frequency band can be divided into high frequency, intermediate frequency, low frequency and full band speakers; The form can be divided into external magnetic type, internal magnetic type, double magnetic circuit type and shielded type; according to the magnetic circuit nature, it can be divided into ferrite magnet, neodymium iron boron magnet, aluminum nickel cobalt magnet speaker; according to the diaphragm material Can be divided into paper and non-paper cone speakers ...
(2) Motorized speakers
Motorized speakers are the most widely used in civil audio systems. They use the interaction between the voice coil and a constant magnetic field to make the diaphragm vibrate to sound. Most of the electric woofers are cone type, the mid-range speakers are mostly cone type or dome type, and the tweeters are usually dome type, belt type and horn type.
The cone type speaker has a simple structure and high energy conversion efficiency. The diaphragm material used in it is mainly pulp material, or mixed with human wool, silk, carbon fiber and other materials (or glue) to increase its rigidity, internal damping and waterproof performance. The new generation of electric cone speakers use non-paper diaphragm materials, such as polypropylene, mica carbide polypropylene, carbon fiber braid, bulletproof cloth, hard aluminum foil, CD corrugation, glass fiber and other composite materials, the performance is further improved.
Dome speakers are divided into soft dome and hard dome. The dome of the soft dome loudspeaker uses silk, silk, cotton cloth impregnated with phenolic resin, chemical fiber and complex materials, which is characterized by soft and reproducible sound quality; , Which is characterized by crisp and clear playback sound quality.
The radiating method of the horn speaker is different from the cone speaker, it is after the diaphragm vibrates, the sound diffuses out through the horn. It is characterized by high electro-acoustic conversion and radiation efficiency, long distance and low distortion, but the playback frequency band and directivity are narrow.
The voice coil of the band speaker is directly made on the entire diaphragm (aluminum table gold or polyimide film, etc.), and the voice coil is directly coupled with the diaphragm. The alternating magnetic field generated by the voice coil interacts with the constant magnetic field, causing the band diaphragm to vibrate to radiate sound waves. It is characterized by fast response speed, low distortion, fine playback sound quality and good sense of layering.
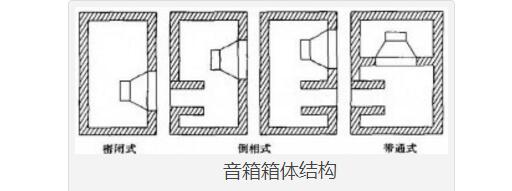
2. CabinetThe cabinet is used to eliminate the acoustic short circuit of the speaker unit, suppress its acoustic resonance, widen its frequency response range, and reduce distortion.
The box structure of the speaker is divided into bookshelf type and floor type, as well as vertical type and horizontal type. The internal structure of the cabinet is also in various forms such as closed type, inverted phase type, belt type, empty paper cone type, labyrinth type, double cavity double opening type, 1/4 wavelength loading type, symmetric drive type and horn type The most common ones are closed type, inverted type and belt type, as shown in the figure below.
The frequency divider is divided into a power frequency divider and an electronic frequency divider. The main functions are frequency band division, amplitude frequency characteristic and phase frequency characteristic correction, impedance compensation and attenuation.
The power divider, also called passive post-stage divider, divides the frequency after the power amplifier. It mainly consists of passive components such as inductance (L), resistance (R), capacitor (C) and other filter components, and sends the audio signals of each frequency band to the corresponding frequency band speakers for playback. Its characteristics are low production cost, simple structure, suitable for amateur production, but large insertion loss, low efficiency, and poor transient characteristics.

Electronic frequency divider, also called active front-end frequency divider, is composed of various resistance-capacitance elements and active devices such as transistors or integrated circuits. It is an analog placed in the signal line of preamplifier and power amplifier. The electronic filter can divide the audio signal output by the preamplifier into different frequency bands, and then send it to the power amplifier for amplification processing. It is characterized by spectrum balance in each frequency band, small mutual interference, large output dynamic range, a certain amplification capability, and low insertion loss. But because the circuit is more complicated, it is more difficult for amateur production than the power divider.
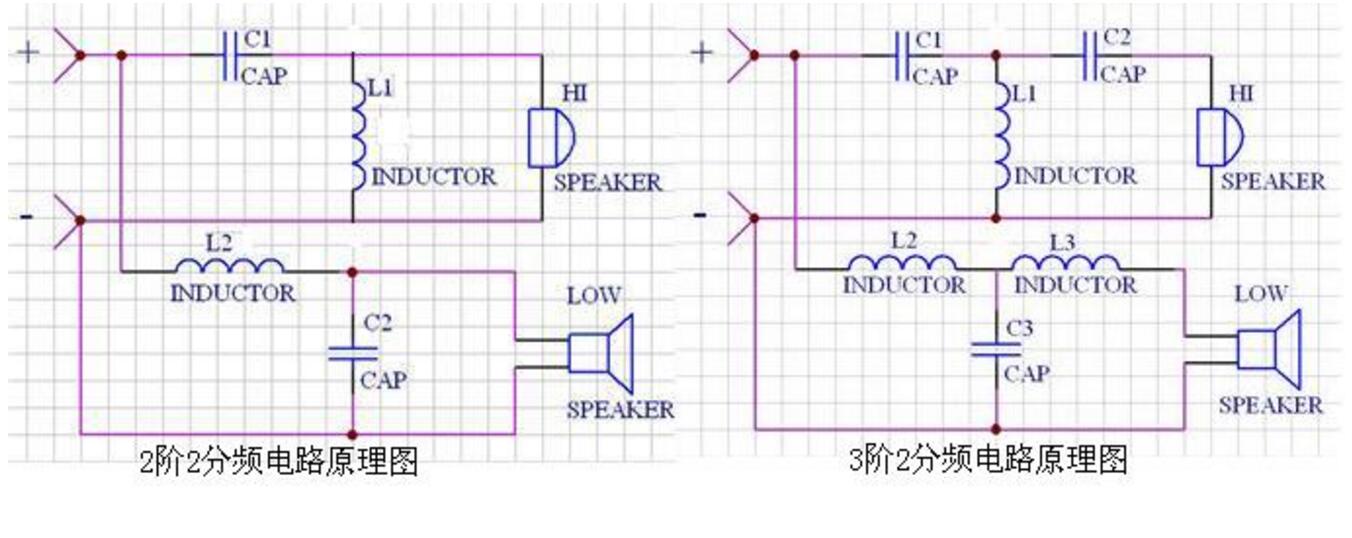
The frequency divider can be divided into two frequency division, three frequency division and four frequency division according to the frequency division frequency band. Two-way frequency is to divide the entire frequency band of the audio signal into two bands of high frequency and low frequency; three-way frequency is to divide the entire frequency band into three bands of high frequency, intermediate frequency and low frequency; four-way frequency divides the three-way frequency into one Ultra-low frequency band. The speaker is produced under amateur conditions, mainly divided by two and three.
The crossover point and crossover slope are the crossover frequencies (crossover frequency) that directly affect the crossover.
Crossover point refers to the intersection of the frequency response curves of two adjacent speakers (such as treble and bass in the second frequency division, treble and midrange in the third frequency division, midrange and bass) at a certain frequency, usually The frequency at half of the power output of the two speakers (ie, a 3dB point) is determined according to the frequency characteristics and distortion of the speaker and each speaker. Usually, the frequency dividing point of the two-way frequency divider is between 1kHz and 3k, and the three-way frequency point is two frequency points of 250Hz to 1kHz and 5kHz.
The crossover slope (also called the attenuation slope of the filter) is used to reflect the falling slope of the frequency response curve below the crossover point, expressed in decibels / octave (dB / oct). It is divided into first order (6dB / oct), second order (12dB / oct), third order (18dB / oct)) and fourth order (24dB / oct)), the higher the order, the slope of the frequency curve after the frequency division point The bigger. The more commonly used is the second-order crossover slope. High-order crossovers can increase the slope but have a larger phase shift. Low-order crossovers can produce a gentler slope and a good transient response, but the amplitude-frequency characteristics are poor. Deciding the order of high and low frequency filtering should mainly consider the problem of good connection of the phase of the speaker itself at the crossover point.
The internal structure of seven kinds of speakersIt is the simplest speaker system. It was proposed by FrederI Ck in 1923. Simply put, the speaker unit is installed in a fully sealed box. It can completely isolate the forward radiated sound wave and the backward radiated sound wave of the speaker, but due to the existence of the enclosed box, the rigidity of the resonance of the moving mass of the speaker is increased, and the minimum resonance frequency of the speaker is increased.
The sound quality of the enclosed speakers is a little deep, but the bass analysis is good. When using ordinary hard folding ring speakers, in order to obtain satisfactory bass reproduction, a large-volume cabinet needs to be used. Most of the new enclosed speakers use a high Q value. Compliant speakers. Using the elastic effect of the quality of compressed air enclosed in the box, although the speaker is installed in a smaller box, the air cushion behind the cone will exert a counter-force on the cone, so this small enclosed speaker is also called an air cushion speaker .
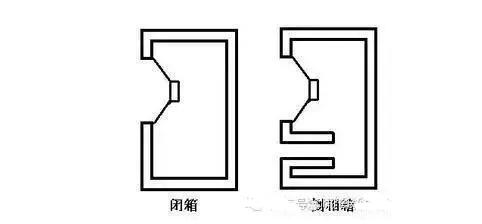
Bass reflex speakers are also called inverted speakers, invented by Thuras in 1930. There is a sound outlet opening in its load on a panel of the cabinet. There are many positions and shapes of the opening, but most of them are also equipped with sound ducts in the hole. The relationship between the internal volume of the cabinet and the sound tube hole, according to the principle of resonance, produces resonance at a specific frequency, called anti-resonance frequency. The sound wave radiated backward by the speaker is inverted by the duct, and then radiated to the front from the sound outlet, and superposed in the same phase as the sound wave radiated forward by the speaker.
It can provide a wider bandwidth than the closed type, with higher sensitivity and less distortion. Ideally, the lower limit of the low-frequency playback frequency can be as much as 20% lower than the speaker resonance frequency. This kind of speaker can reproduce rich bass with a small cabinet, which is the most widely used type at present.

It is essentially a deformation of an inverting sound box. It is filled with sound absorbing material or structure in the sound outlet duct and acts as a semi-closed box to control the inverting effect and make it buffer to reduce the anti-resonance frequency to broaden the bass playback. Frequency band.
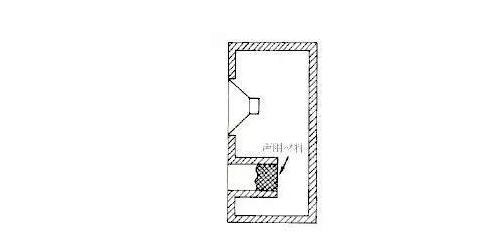
It is named after the transmission line of classical electrical theory. There is a sound tube made of sound-absorbing wall board behind the speaker, and its length is 1/4 or 1/8 of the wavelength of the low-frequency sound to be raised.
In theory, it attenuates the sound waves coming from behind the cone to prevent it from being reflected to the open end and affect the sound radiation of the woofer, but in fact the transmission line type speaker has a slight damping and tuning effect, increasing the speaker at or near the resonance frequency Acoustic output, and reduce the amount of stroke while enhancing bass output. Usually the sound ducts of such speakers are mostly stacked in a labyrinth, so they are also called labyrinth or labyrinth.
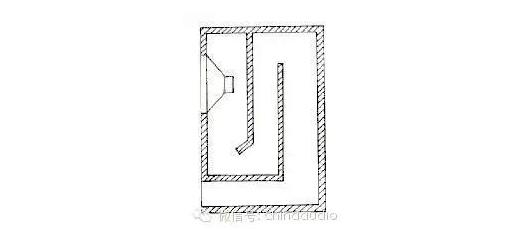
It is a branch of the bass reflex speaker, also known as the empty paper cone speaker. It was published by Olson and Preston in the United States in 1954. Its opening sound outlet consists of an empty paper cone (passive cone) without a magnetic circuit and voice coil. ) Replacement, the radiation generated by the vibration of the passive cone and the forward radiated sound of the speaker are in the same phase of working state, and the resonance of the composite sound and the quality of the passive cone formed by the air in the cabinet and the support assembly of the passive cone form a resonance to enhance the bass.
The main advantage of this kind of speaker is to avoid the unstable sound reflected by the sound hole. Even if the volume is not large, a good sound radiation effect can be obtained, so the sensitivity is high, which can effectively reduce the working amplitude of the speaker and the impact of standing waves Small, clear and transparent sound.
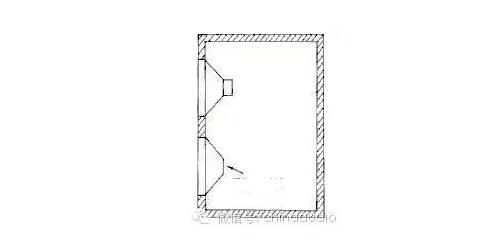
It is a box structure between the closed type and the bass reflection type. Henry Lang of the United States published it in 1953. Its output is output by the sound hole driven by one side of the cone, and the other side of the cone is connected to a closed box. coupling.
The advantage of this kind of speaker is that the amount of air pushed by the speaker is greatly increased at low frequencies. Because the coupling cavity is a tuned system, when the cone movement is restricted, the output of the sound outlet does not exceed the sound output of the individual cone, which broadens the low frequency. Range, so the distortion is reduced and the withstand power is increased. The A · S · W (AcoustICSuperWoofer) speaker released by Koshima Kawashima of Lo-d, Japan in 1969 is a coupled cavity speaker suitable for reproducing low-frequency bass with a small-diameter long-stroke speaker without distortion.
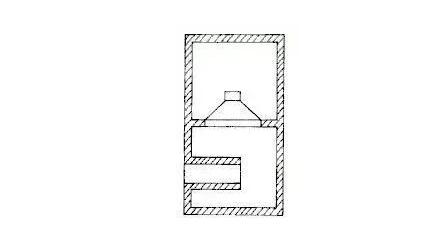
For household models, the folded horn is mostly used. Its horn horn is coupled with a large air load at the mouth, the diameter of the drive end is very small, the back of this speaker is fully sealed, and the pressure in the chamber is much. On the back of the speaker cone.
In order to maintain the balance of the front and rear pressure of the cone, the inverted horn is installed in front of the speaker. Folded horn speaker is a derivative of the inverted speaker, its sound effect is better than the general bass reflex speaker of the enclosed speaker.
Plastic Pa Speaker,15 Inch Speaker,15 Inch Double Magnet Speaker,Pa Sound System
NINGBO LOUD&CLEAR ELECTRONICS CO.,LIMITED , https://www.loudclearaudio.com