Recently, a recent paper published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA Ophthalmology) shows that AI researchers have newly developed an algorithm that can automatically detect the underlying causes of blindness in children with far more accuracy than humans. Doctors.
The study can help more preterm infants to prevent retinopathy of prematurity (ROP). Stevie Wonder is blind because of the disease.
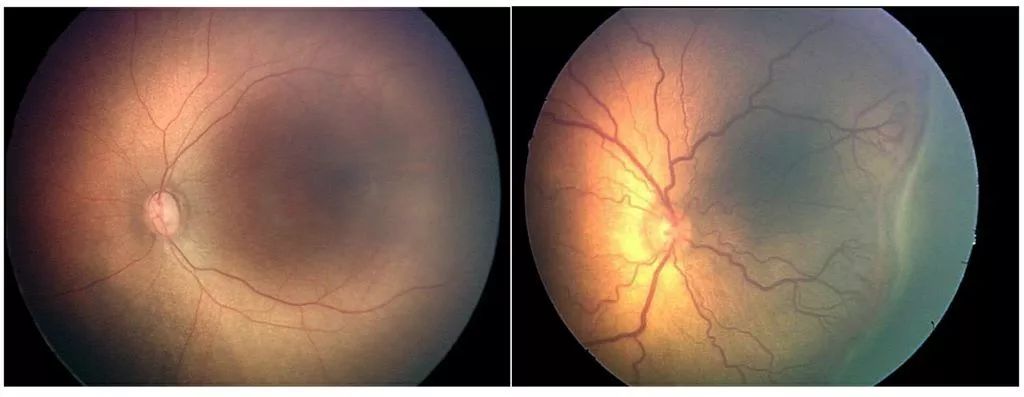
The algorithm can diagnose the presence of the disease by recognizing the baby's eyeball photo, with an accuracy rate of 91%. However, during the same period of testing, a control group of eight doctors diagnosed the same eyeballs with an accuracy of only 82%.
“In the field of diagnosing retinopathy of prematurity, well-trained ophthalmologists have been very scarce, so the corresponding care is also difficult to achieve, even in the United States. Many children in the world have not had time to diagnose,†said Michael Chiang, research co-leader of the study, explained. Michael is a professor of clinical epidemiology and medical information at the Oregon Health University (OHSU) School of Medicine.
"The algorithm deciphers the knowledge system of recognizing retinopathy of prematurity by experienced ophthalmologists and forms a mathematical model, so even clinical sounds without such experience can be used to timely and accurately diagnose infants." Another co-leader, Jayashree Kalpathy, said. Kalpathy is an associate professor of radiology at Harvard Medical School.
Artificial intelligence can make machines think like humans and is now being applied to the medical field. Last month, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) agreed to use AI equipment to detect eye diseases caused by diabetes. Others have also tried to develop computer systems to diagnose retinopathy of prematurity, but they have not yet reached the diagnostic level of human doctors.
The new algorithm developed this time uses deep learning technology to simulate the way human vision perceives the world, including the ability to recognize objects. Massachusetts General Hospital researchers combined two AI models to develop the algorithm, and Oregon Health University researchers used a variety of reference standards to train the algorithm.
First of all, they used 5,000 pictures of children who were kept at the ophthalmologist to train algorithms to identify retinal blood vessels. Then they trained the algorithm to distinguish healthy blood vessels from diseased blood vessels. Then they compared the accuracy of algorithm recognition with the same sample conditions. The accuracy rate of human experts, and found that the accuracy of the algorithm is higher than the average human expert doctor.
The research team is currently working with an Indian company to study whether the algorithm can achieve the same results as the US sample of children in the diagnosis of retinopathy of preterm infants in Indian babies. At the same time, researchers are also exploring whether the algorithm can also diagnose the health of other parts of the retina other than blood vessels. In short, they ultimately hope that doctors can use this technology in clinical diagnosis.
Shenzhen GL-COM Technology CO.,LTD. , https://www.szglcom.com